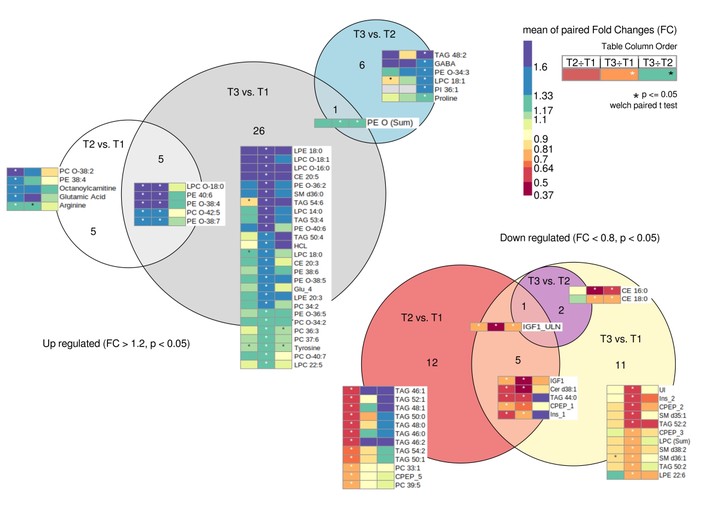
Despite marked insulin resistance, patients with active acromegaly have low hepatocellular lipid content (IHL) and an unfavourable hepatic lipid composition (UI). Inadequate mitochondrial activity in the liver might counteract lipid accumulation in the liver. The purpose of this study was to understand changes in hepatic metabolism, and lipidomic profile with therapy of acromegaly
Method
- Thirteen subjects (5 female, age: 48,3+-12,7years) with active acromegaly - which was diagnosed by elevated serum IGF-1 concentrations and lack of Growth Hormone (GH) level suppression (>1 ng/ml) after ingestion of 75 mg glucose during a standardized two-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
- Participants underwent 31P/1H-7T-MR-spectroscopy of the liver, an OGTT, as well as plasma metabolomic and lipidomic profiling at baseline and twelve months after inclusion
Insights
- This study shows that with biochemical improvement of acromegaly, the lipid composition as well hepatic mitochondrial activity changes significantly
- There might be a causal relationship between Growth Hormone (GH) excess and hepatic lipid accumulation
- Reduction in lipid classes, like ceramides and sphingomyelins, which are associated with insulin resistance indictes relationship between insulin resistance and acromegaly